离散概率

概念
运算
加
- if $A\cap B = \emptyset$
- $P(A\cup B) = P(A)+P(B)$
Theorem
Let E1 and E2 be events in the sample space $\Omega$.Then
$P(E_1\cup E_2)= P(E_1)+P(E_2)-P(E1\cap E2)$
证明:
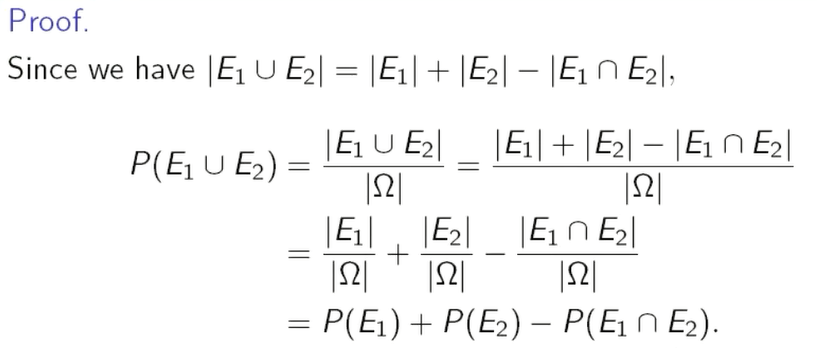
但这个证明不是很严谨,默认这是均匀分布的,才能够这么写
应该这么写
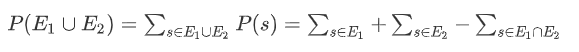
推论
- if $E_i\cap E_j=\emptyset $ for $\forall i,j$ then
- $P(\bigcup{i=0}^{\infty})=\sum{i=1}^{\infty}P(E_i)$
- 三个事件发生的概率—— 容斥原理
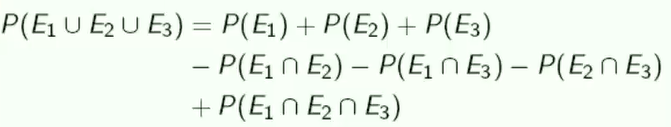
减
$A\subset \Omega$
$P(\overline A)=P(\Omega)-P(A)=1-P(A)$
证明
分清楚对立事件和互斥事件。对立事件是:不是你就是我,互斥时间是:两者没有交集
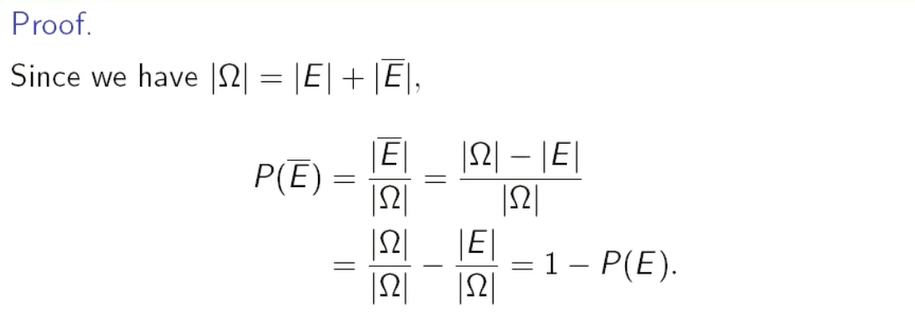
例子: 正难则反
乘
- 如果A和B是相互独立的,那么
- $P(A\cap B)=P(A)\cdot P(B)$

- $P(A)=P(B)=P(C) = 0.5$
- $P(A\cap B) = P(A\cap C) = P(B\cap C) = 0.25$ 两两独立
- $P(A\cap B\cap C) = 0.25$ 这不是相互独立
- 所以这里有个重要的概念——独立
- 一类是两两独立,一类是相互独立
相互独立一定能导出两两独立,但是两两独立并不能导出相互独立。
所以上面ABC相互独立而不是两两独立
结论
- 注意点:两个事件独不独立,是看他是否满足$P(A\cap B) = P(A)\cdot P(B)$ 跟集合没有关系,所以别用韦恩图判断,是要搞脑子的。
- 就比如说一个2位数,全集为{1,2},P(E)=”第一个数字为1”,P(F)=”第二个数字为2”,那么$P(E\cap F) = \frac{1}{2}\cdot \frac{1}{2}=\frac{1}{4}$
- $P(\overline F)$是第二个数字不为2,那么只能为1,$P(E\cap \overline F) = \frac{1}{2}\cdot \frac{1}{2}=\frac{1}{4}$
- $P(\overline E)$是第一个数字不为1,那么只能为2,$P(\overline E\cap F) = \frac{1}{2}\cdot \frac{1}{2}=\frac{1}{4}$
- $P(\overline E\cap \overline F) = \frac{1}{2}\cdot \frac{1}{2}=\frac{1}{4}$
- 又如:

- 又如:

- 又如

解题逻辑:我们要先列出P(E)再列出P(F),最后与$P(E\cap F)$ 作比较
条件概率
- The conditional probability of A given B. denoted by P(A|B),is compute as
- $P(E|F)=\frac{P(E\cap F)}{P(F)}$
所以说是把样本空间改了一下,把原来的$\Omega$换成了我们的F
Question: What is the conditional probability that a family with two children has two boys, given they have at least one boy? Assume that each of the possibilities BB, BG, GB, and GG is equally likely.
Solution: Let E be the event that a family with two children has two boys, and let F be the event that a family with two children has at least one boy. It follows that E = {BB}, F = {BB; BG; GB}, and E $\cap$ F = {BB}.
Because the four possibilities are equally likely, it follows that P(F) = 3/4 and $P(E\cap F) = \frac 1 4$.
We conclude that
P(E|F) = P(E $\cap $ F)/P(F) = $\frac 1 3$
注意
- 当A 和B都是独立的时候,P(E|F)=P(E)
答题格式,我们一定要分清楚 什么事件是E,什么事件是F,声明条件的是F,发生什么情况的是E。
然后我们求出$P(E\cap F)$
最后$P(E|F) = P(E\cap F)/P(F) $
What is the conditional probability that exactly four heads appear when a fair coin is flipped five times, given that the first flip came up heads/tails?
按照上面的步骤,我们知道F是第一次硬币为正面/反面,概率都是1/2
$P(E\cap F)$ 则是出现正面在5次中占据4次,那么如果第一次为正面,那么后面四次只要选3次即可,$P(E\cap F) = \frac{P(4,3)}{2^5} = \frac{1}{8} $
如果第一次为反面,那么后面四次必须全部为正面,那么$P(E\cap F)= \frac{1}{32}$
所以 $P(E|F) = P(E\cap F)/P(F) = \frac{1}{4}$ 或者 $\frac{1}{32}$
我们要特别注意:in a row, consecutive 这类的单词,因为这说明某些特定数字是连续的!
全概率公式(Total probability theorem)
- $P(E\cap F) = P(E)\cdot P(F|E)= P(F)\cdot P(E|F)$
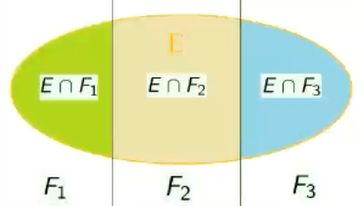
- 通过上面这张图,我们可以得到全概率公式
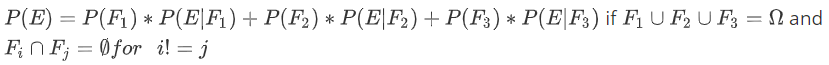
- 可以以此类推.一直到n类,相当于一个分类讨论
- 证明:
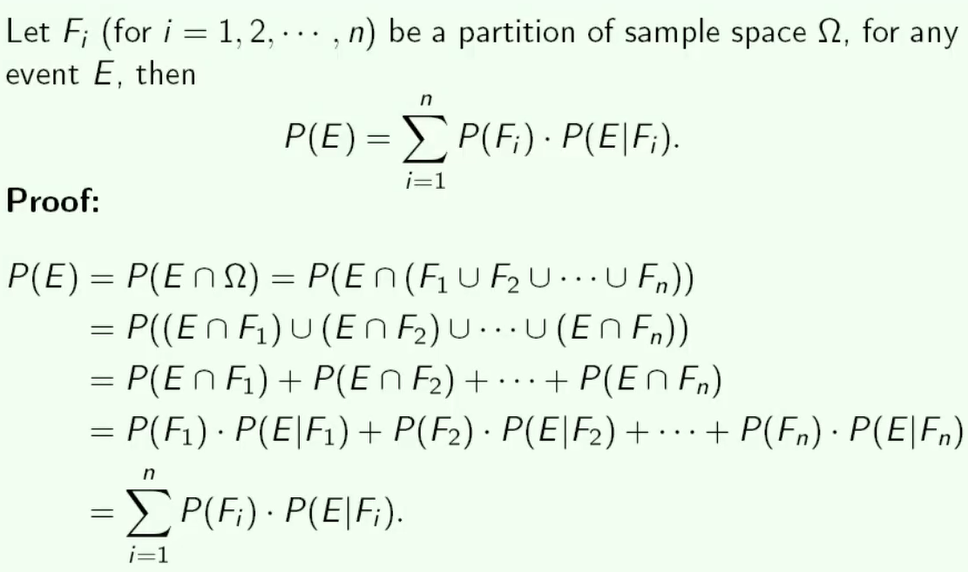
Bayes rule(贝叶斯公式)
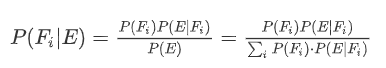
贝叶斯公式的应用
就是通过E来反推、预测 Fi的概率
我们假设Fi要么是男要么是女,E是这个人的属性,我们就可以计算$P(Female|Person)$或者$P(Male|Person)$
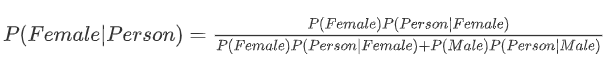
P(Person|Female)的意思就是如果这个人是女性,那么她长头发、高跟鞋的概率为多少。
所以这就是一个分类器,除了预测这是男是女,还可以预测你会不会买这个商品,一封邮件是不是垃圾邮件
这就是机器学习的方法之一,在数据科学领域是经常会用到的一个公式
例题
Question: Suppose we draw two cards from a well shuffed deck. What is the probability the second card in the deck is an ace?
Solution: Let E and F be events that the fi rst and the second cards are Aces, respectively. Hence $E$ and $\overline E$ is a partition of the sample space.
In terms of the total probability theorem, condition on whether the fi rst card is an ace or not:
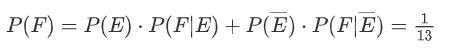
Question: 两根不同的标签,两个人抽签,公平吗?
Solution: 设第二次抽中长的概率为 P(F) = $\frac{1}{2}\cdot 0+\frac{1}{2}\cdot 1 = \frac{1}{2}$ 两个都是如此,所以是公平的,所以说,第二次抽中长的并不是一个条件概率