K-NN 算法
K-NN(K-Nearest Neighbors) 算法也是用来分类的,他直观上十分容易理解:
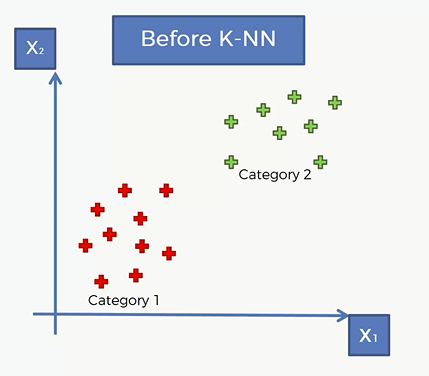
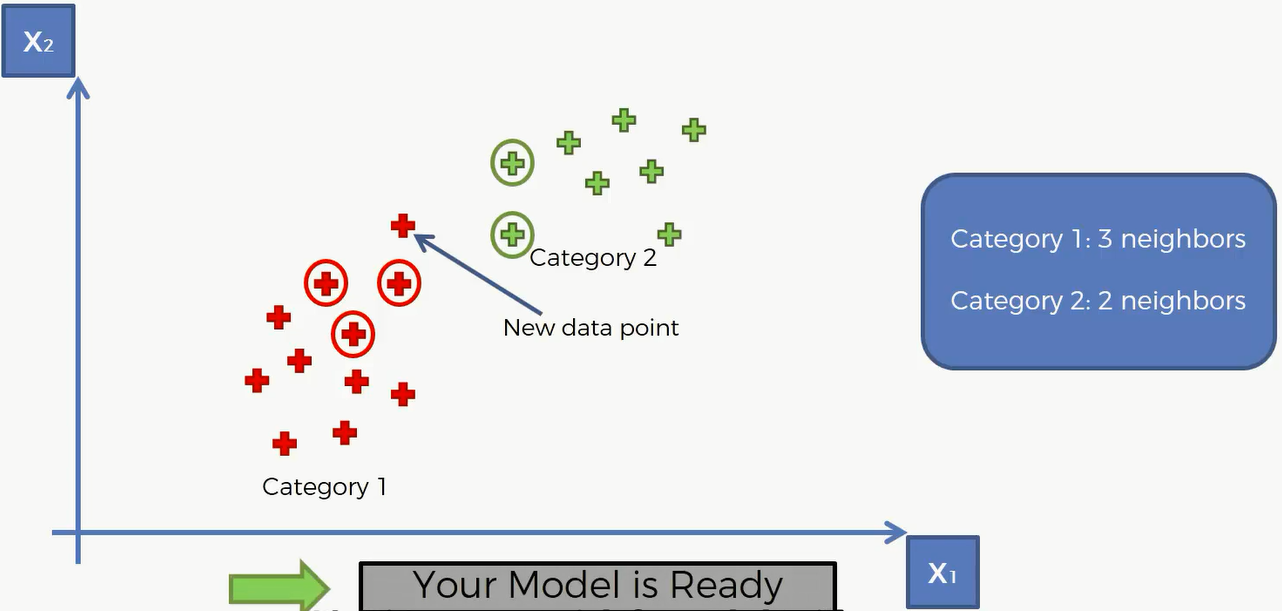
现在有两类,分别用红色的加号和绿色的加号描出,现在我们进来了一个新的数据点,我们的目标就是将这个数据点划到哪一类里面去。
比如说下面这个点经过类K-NN 算法,被划归到红色的那一类取了
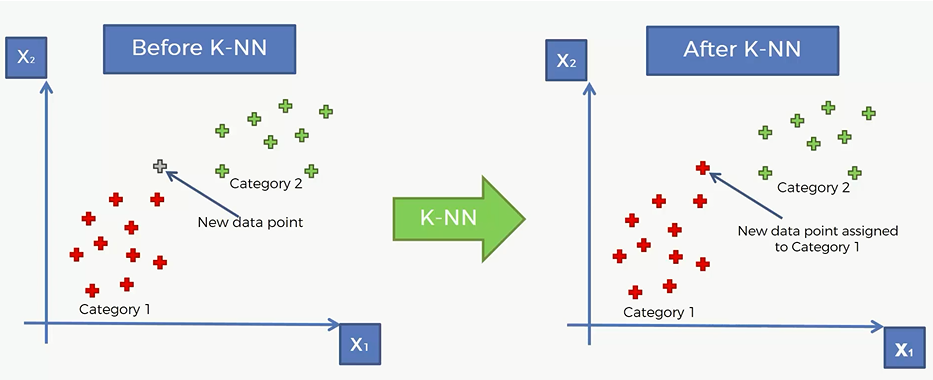
那么K-NN 算法是怎么运作的呢? 其实很简单
- STEP1: Choose the number K of neighbors
- STEP2: Take the K nearest neighbors of the new data point , according to the Euclidean distance
- STEP3: Among these K neighbors ,count the number of data points in each category
- STEP4: Assign the new data point to the category where you counted the most neighbors
结合上面这个写步骤,我们对刚才的例子进行剖析:
我们现决定要选取5个距离这个点最近的邻居
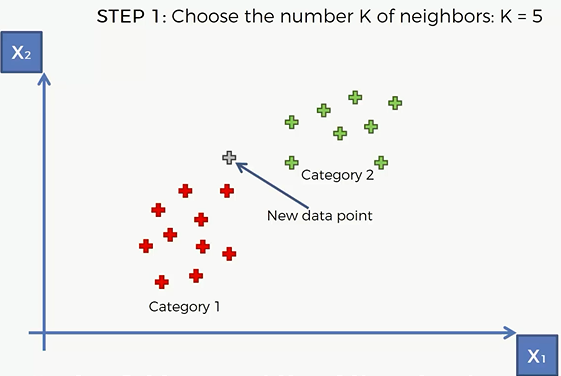
然后计算他和邻居之间的 Euclidean 距离,欧几里得距离的计算公式: $d=\sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2}$
然后计算距离这个点最近5个欧几里得距离。在这5个最近的邻居中,属于红色区域的有3个,属于绿色区域的有2个,那么这个点就会被划分到红色区域当中去。
代码
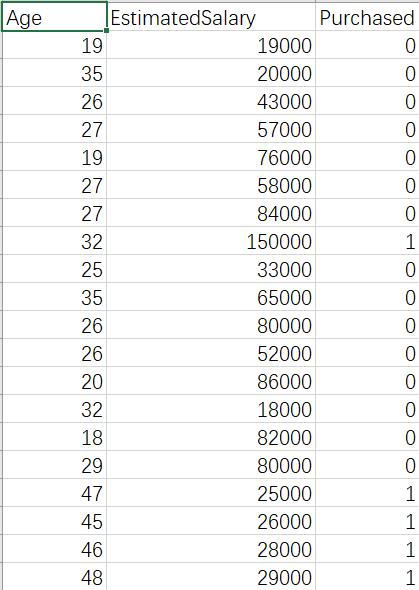
我们使用的数据集:
和逻辑回归的思路是一样的,只是换一个模型而已,所以这里略去重复的代码
Training the K-NN model on the Training set
n_neighbors =5 比较常用当然也可以多试试别的值来取最高的准确率
metric = ‘minkowski’ (闵可夫斯基) 就是说距离计算公式运用闵氏距离,是欧氏空间中的一种测度,被看做是欧氏距离和曼哈顿距离的一种推广。 $(\sum_{i=1}^n |x_i-y_i|^p)^{\frac{1}{p}}$
p=2就是 上面这个公式的 p
1 | from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier |
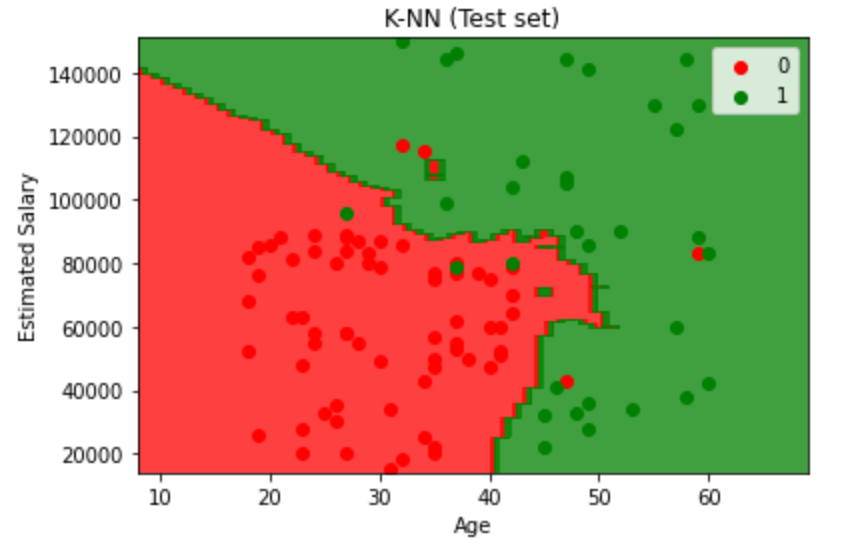
看一下这个模型的混淆矩阵和准确分数:
1 | from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score |
混淆矩阵:
[[64 4]
[ 3 29]]
准确度:0.93
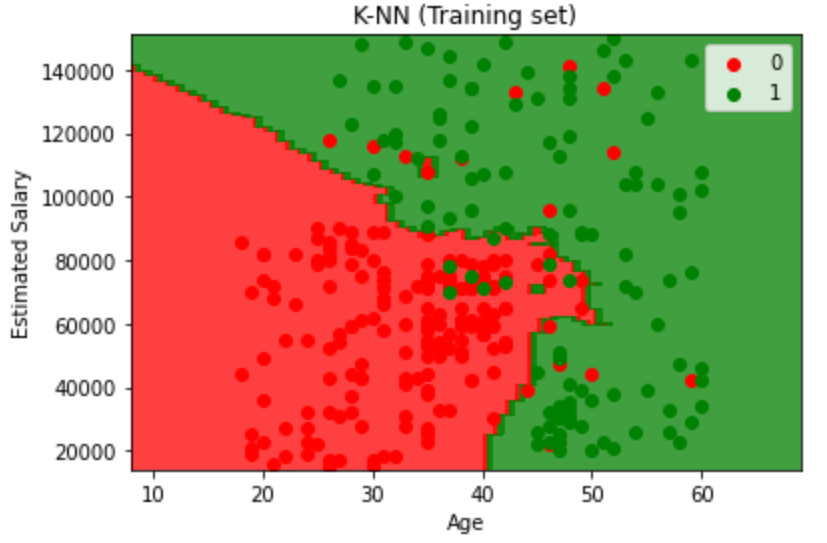
Visualising the Training set results
最后用可视化图来看一下结果:
1 | from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap |
1 | from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap |