设计模式2-结构型模式
Composite Pattern
组合模式(Composite Pattern),又叫部分整体模式,是用于把一组相似的对象当作一个单一的对象。
The Problem
比如说,在PPT中我创建了两个长方形,两个圆形,那么我们可以选中两个长方形将它们同时移动或者缩放;同样的,我们甚至可以选中四个物体同时移动缩放
除此之外,最经典的例子是文件夹与文件的表示,一个文件夹(容器对象)既可以存放文件夹(容器对象),也可以存放文件(叶子对象)。如果把树的每个节点摊平,那就是List。而树结构,则是更能直观的体现每个节点与整体的关系。
为什么需要这个模式呢?它的目的是什么?
可以体现出类与类之间的层级结构
主要是想要对外提供一致性的使用方式,即使容器对象与叶子对象之间属性差别可能非常大,我们希望抽象出相同的地方,一致的处理。
Solution
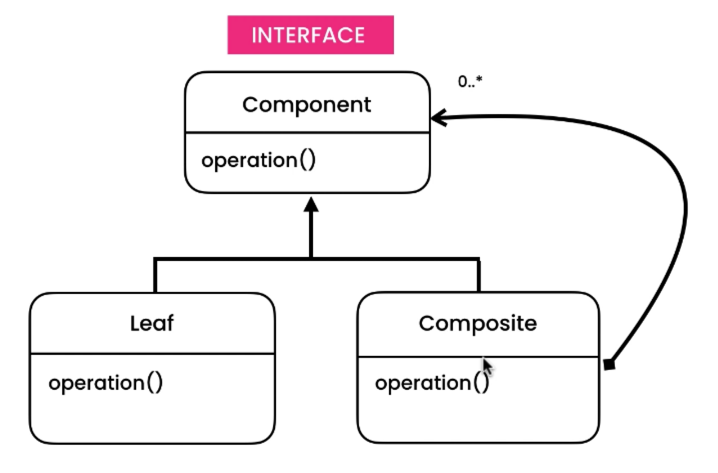
组合模式中一般有以下三种角色:
- 抽象构件(
Component):一般是接口或者抽象类,是叶子构件和容器构件对象声明接口,抽象出访问以及管理子构件的方法。 - 叶子节点(
Leaf):在组合中表示叶子节点对象,叶子节点没有子节点,也就没有子构件。 - 容器构件(
Composite):容器节点可以包含子节点,子节点可以是叶子节点,也可以是容器节点。
Implementation
1 | public interface Component { // Component接口,容器和叶子都需要实现它 |
小结
组合模式的优点:
- 可以分层次定义复杂对象,表示局部和全部,客户端可以忽略不同的节点的差异。
- 从高层次调用,可以很顺畅的调用到每一个局部,一致性比较强。
- 节点自由搭配,灵活度比较高。
缺点:
- 在使用组合模式时,其叶子和组合节点的声明都是实现类,而不是接口,违反了依赖倒置原则。
使用场景:
- 希望忽略每个部分的差异,客户端一致使用
- 需要表现为树形结构,以表示“整体-部分”的结构层次。
Exercise
We’re building an application for an incident management organization. When an incident (eg fire) occurs, one or more teams may be deployed to attack the incident.
A team often includes a truck and one or more human resources. It can also include a sub team. For example, for a medium-sized incident, we may need to deploy two teams and each team may contain a truck and two persons.
Team
Sub Team 1
- Truck
- Human Resource
- Human Resource
Sub Team 2
- Truck
- Human Resource
- Human Resource
Look at the current implementation of our application in the composite package.
What are the problems with this implementation? Refactor the code using the composite pattern.